New shark species named after Eugenie Clark
A newly discovered shark species has been named after Eugenie Clark, the renowned pioneer in shark biology.
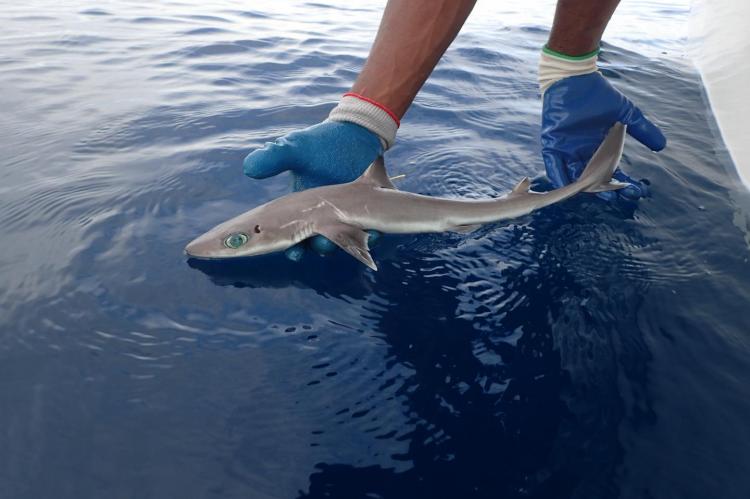
The newly discovered species was named Genie's Dogfish (Squalus clarkae) in honour of Eugenie Clark, the pioneer in shark biology renowned for her work on shark behaviour.
Identified from the Gulf of Mexico and the western Atlantic Ocean, the shark was initially labelled as Squalus mitsukurii. It was through genetic testing and morphology that the research team discovered that this was a new species. Confirmation of this was announced in the journal Zootaxa this month.
“Deep-sea sharks are all shaped by similar evolutionary pressure, so they end up looking a lot alike. So we rely on DNA to tell us how long a species has been on its own, evolutionarily, and how different it is," said Florida Institute of Technology assistant professor and shark biologist Toby Daly-Engel.
Naming this particular shark species after Clark is apt, as she was very familiar with the Gulf of Mexico, where Genie's Dogfish was found.
"Genie established Mote [Mote Marine Laboratory] and she lived on the Gulf of Mexico coast. She did a lot to advance our understanding of marine biodiversity there. So naming the dogfish shark from the Gulf of Mexico after her is the most appropriate thing in the world,” said Daly-Engel.
Lead author and marine scientist Mariah Pfleger from Oceana highlighted the increasing threats faced by sharks at greater depths like Genie's Dogfish.
"Many fisheries around the world are starting to fish in deeper and deeper waters and unfortunately, much less is known about many of the creatures that live in the deep. The first step to successfully conserving these species that live in deeper waters, like Genie’s Dogfish, is finding out what is down there in the first place,” she said.